How To Repair Cardiac Pseudo Aneyrism
A rare withal serious complication of myocardial infarction is left ventricular pseudoaneurysm that requires urgent intervention to avert unforeseeable fatal rupture. Here, we present a successful repair of posterolateral and basal left ventricular pseudoaneurysm case, using a modified Dor technique.
pseudoaneurysm, dor technique, left ventricular geometry
Rupture of the left ventricular (LV) wall is a rare but disastrous complication of myocardial infarction [i,ii]. It is inappreciably contained past hematoma and pericardial adhesions creating a pseudoaneurysm (PsA) [1]. Urgent surgical repair is required to prevent catastrophic rupture. Surgical repair aims to exclude the necrotic myocardium and aneurysmal area with a patch to preserve the LV geometry and performance [three]. We report a case of LV PsA that was surgically repaired with a modified Dor technique.
A 74-twelvemonth old male patient with no significant by medical history was presented with a 6-week history of dyspnea. A breast 10-ray was performed to evaluate symptoms that depicted an enlarged cardiac silhouette. This was followed by transthoracic echocardiography that showed huge posterolateral and basal LV pseudoaneurysm (7x10 cm), LV systolic dysfunction (ejection fraction (EF) ≤ twenty%), mild mitral regurgitation (MR) and Aortic insufficiency (AI). Consequently, the patient underwent left heart catheterization that revealed a totally occluded left circumflex coronary artery, eighty% stenotic lesion in the left inductive descending artery, intimal irregularity in the right coronary avenue, and big posterobasal and lateral LV pseudoaneurysm.
On the post-obit solar day, subsequently Intera aortic balloon pump insertion (IABP), the patient underwent surgical repair of LV PsA (Dor procedure) using the modified technique forth with bypass grafting of the left coronary organisation lesions.
Upon opening the pericardium, dumbo fibrinous adhesions were constitute suggestive of reactive pericarditis secondary to contained LV rupture. The pericardial adhesions were gently dissected. After initiating cardiopulmonary bypass, the heart was lifted upward and contained rupture of a big posterolateral LV PsA was known. The posterior wall of LV was opened over the PsA area and an organized thrombus, which was sealing off the rupture site, was removed. The diagnosis of LV PsA was confirmed past the absence of myocardial components in the wall (east.g. thinned necrotic myocardium), formed by organized hematoma and pericardial adhesions. Within the LV cavity, the mitral valve was intact, while the posterior papillary muscle appeared normal with hyperaemic borders suggestive of recent ischaemic injury. The Dacron patch was prepared. Interrupted 2-0 Etiband-pledged mattress sutures were placed around the neck of the PsA, and then passed through the Dacron patch and tied downward (Figure 1A and 1B).
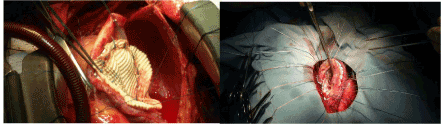
Figure 1. Repair of PsA with the Dacron patch
Besides, the patient underwent bypass grafting of the left anterior descending artery using the left internal mammary avenue. The cross-clamp time was 135 minutes, total cardiopulmonary bypass time was 156 minutes, and the total procedure time was iv hours.
IABP extract later on 52 hours. Postoperative echocardiography showed improvement of LV function (EF ≤ 30%), mild MR, and balmy AI. Also, the Dacron Patch appeared intact with no paradoxical bulging during systole and no flow across (Figure two). The patient was discharged on the tenth postoperative twenty-four hour period.
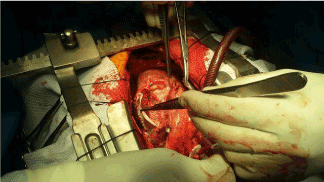
Figure 2. Reinforcement of PsA repair with the Gore-tex patch
Patients with LV PsA commonly nowadays with angina or congestive eye failure symptoms but tin also present with cardiac tamponade [4].
In this example study, the patient presented with dyspnea, while he had no history of cardiac illness before the time of ischemic injury. However, operative findings were suggestive of a sub-acute presentation organized thrombus and thickened pericardial tissues sealing off the LV rupture site. Besides, the rupture site edges appeared thickened and scarred. Differentiation between true and pseudo-LV aneurysms is crucial for the timing of intervention.
The bones principle of the Dor procedure is to exclude the LV aneurysmal office with a round patch to restore the physiological geometry of the LV cavity and to better its function [5,6]. The two patch techniques may provide an boosted do good over the traditional unmarried-layer patch past existence less prone to bulging out during systole; hence, they result in better preservation of the LV geometry and function, especially in the early postoperative menstruum. To our cognition, this is the first reported case of LV PsA repair using two patches. Long-term follow-upwards is needed to evaluate the effect of the two patch techniques on LV remodeling.
- Zoffoli G, Mangino D, Venturini A, Terrini A, Asta A, et al. (2009) Diagnosing left ventricular aneurysm from pseudo-aneurysm: A case written report and a review in literature. J Cardiothorac Surg 4:1-v. [Crossref]
- Hosseinzadeh-Maleki M, Valizadeh Due north, Rafatpanah N, Moezi SA (2015) Survival later left ventricular gratis wall rupture due to astute myocardial infarction. ARYA Atheroscler 11: 310-313. [Crossref]
- Elgharably H, Halbreiner MS, Shoenhagen P, Navia JL (2016) Repair of the left ventricular pseudoaneurysm with the triple patch technique (Empanada Patch). Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 22:116-117. [Crossref]
- Hulten EA, Blankstein R (2012) Pseudoaneurysms of the heart. Circulation 125:1920-1925. [Crossref]
- Buckberg GD, Dor V, Di Donato Chiliad, Sabatier 1000, Montiglio F, et al. (2001) Ventricular shape and function in health and diseaseleft ventricular reconstruction past endoventricular round patch plasty repair: A 17-year experience. Sem Thor Cardiovas Sur 13: 435-447.
- Dor Five, Saab M, Coste P, Kornaszewska Thousand, Montiglio F (1989) Left ventricular aneurysm: A new surgical arroyo. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 37: eleven-19. [Crossref]
Editorial Information
Editor-in-Chief
Andy Goren
University of Rome, Italy
Article Blazon
Case Report
Publication history
Received date: June 17, 2022
Accustomed date: June 26, 2022
Published date: June thirty, 2022
Copyright
©2020 Junaid One thousand. This is an open-access commodity distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted utilize, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation
Mahmood Hosseinzadeh Maleki, Nahid Azdaki (2020) The psychological impact of COVID-xix pandemic on Pakistani population: Managing challenges through mental health services. Clin Example Rep Rev, 6: DOI: x.15761/CCRR.1000483
Corresponding author
Alireza Rahmani Motlaq
Birjand University of Medical Sciences, Birjand, Iran
E-mail : bhuvaneswari.bibleraaj@uhsm.nhs.u.k.

Figure one. Repair of PsA with the Dacron patch

Effigy 2. Reinforcement of PsA repair with the Gore-tex patch
How To Repair Cardiac Pseudo Aneyrism,
Source: https://www.oatext.com/repair-of-the-left-ventricular-wall-pseudoaneurysm-following-myocardial-infarction-simple-modified-dor-technique.php
Posted by: breesewiliturkered80.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Repair Cardiac Pseudo Aneyrism"
Post a Comment